Understanding Angioplasty: A Life-Saving Procedure
Angioplasty, hailed as a medical marvel, has transformed the landscape of cardiovascular disease treatment, especially concerning obstructed or constricted arteries. This minimally invasive procedure holds the power to reinstate proper blood circulation to the heart, alleviating symptoms and fostering enhanced heart wellness. In this blog post, we will explore the intricacies of angioplasty, its advantages, potential risks, and the path to recovery, all while acknowledging the expertise of the best cardiologist doctor in Greater Kailash.
What is Angioplasty?
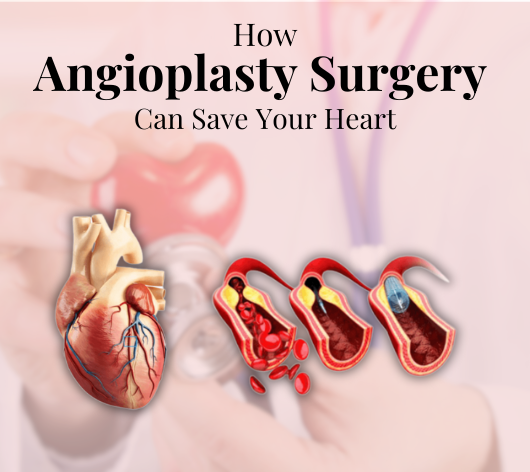
Angioplasty, or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), stands as a vital procedure aimed at widening narrowed or obstructed arteries. It serves as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with cardiovascular issues, especially in Greater Kailash. Under the expert guidance of the best cardiologist doctor in Greater Kailash, angioplasty emerges as a cornerstone in the fight against atherosclerosis—a condition characterised by the accumulation of plaque within arteries, impeding blood flow to the heart. Without timely intervention, the consequences of atherosclerosis, including chest pain (angina) and potentially fatal heart attacks, loom large.
During angioplasty, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the groin or wrist, and threaded up to the blocked artery in the heart. A tiny balloon attached to the catheter is then inflated at the site of the blockage, pushing the plaque against the artery walls and widening the artery. In some cases, a stent, a small mesh tube, may be inserted to help keep the artery open.
Benefits of Angioplasty:
- 1. Improved Blood Flow: Angioplasty restores blood flow to the heart muscle, relieving symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
- 2. Prevention of Heart Attack: By opening blocked arteries, angioplasty reduces the risk of a heart attack caused by a complete blockage of blood flow.
- 3. Enhanced Quality of Life: Patients often experience a significant improvement in their quality of life after angioplasty, with increased energy levels and ability to perform daily activities.
- 4. Minimally Invasive: Compared to traditional open-heart surgery, angioplasty is less invasive, resulting in shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and fewer complications.
Risks and Complications:
While angioplasty is generally considered safe, like any medical procedure, it carries certain risks. These may include:
- Bleeding or bruising at the catheter insertion site
- Damage to blood vessels or the heart
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye used during the procedure
- Blood clots or re-narrowing of the treated artery
It's essential to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider and understand the potential benefits and alternatives before undergoing angioplasty.
Recovery and Aftercare:
After angioplasty, patients are usually monitored closely for a few hours to ensure there are no complications. Most people can return home the same day or the next day. However, it's essential to follow your doctor's instructions for a smooth recovery, which may include:
- Taking medications as prescribed, such as blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs
- Making lifestyle changes, including adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress
- Attending follow-up appointments with your cardiologist to monitor your progress and adjust treatment if necessary
Conclusion:
Angioplasty is a highly effective treatment for coronary artery disease, offering relief from symptoms and reducing the risk of heart attack. While it carries some risks, the benefits often outweigh the potential complications, particularly for patients with significant blockages or those who have experienced a heart attack. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of heart disease, consult a healthcare provider to determine if angioplasty is a suitable option for you. Remember, early intervention can save lives and improve long-term heart health.
FAQs about Angioplasty:
1. How long does the angioplasty procedure take?
Angioplasty typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour to complete. However, the duration may vary depending on the complexity of the blockage and other factors.
2. Is angioplasty a permanent solution for blocked arteries?
While angioplasty can effectively widen narrowed arteries and improve blood flow, it is not a permanent solution. Lifestyle changes and medication adherence are crucial for long-term management of heart health.
3. Will I need to stay in the hospital after angioplasty?
Most patients can go home the same day or the next day after angioplasty. However, individuals with certain risk factors or complications may need to stay in the hospital for observation and further treatment.
4. When can I resume normal activities after angioplasty?
You can typically resume light activities within a few days after angioplasty. However, it's essential to avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting for at least a week or as advised by your healthcare provider.
5. Are there any dietary restrictions after angioplasty?
While there are no strict dietary restrictions, following a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium is recommended to maintain artery health. Your healthcare provider or a dietitian can provide personalised dietary recommendations based on your specific needs.