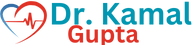
Coronary angiography
Introduction: Coronary angiography, also known as cardiac catheterization, is a diagnostic medical procedure used to visualize the blood vessels (coronary arteries) supplying the heart muscle. This procedure helps healthcare professionals assess the presence of blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities in the coronary arteries, which can be crucial in the diagnosis and management of heart disease. Coronary angiography is often performed as a part of the evaluation process for individuals with chest pain, heart attack symptoms, or known heart conditions.
Key Features of Coronary Angiography:
-
Diagnostic Precision: Coronary angiography is a highly precise diagnostic tool, providing detailed images of the coronary arteries to detect any blockages or abnormalities.
-
Guidance for Treatment: The information obtained from the angiography helps cardiologists determine the most appropriate treatment plan, whether it involves medication, lifestyle changes, angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass surgery.
-
Minimally Invasive: The procedure is minimally invasive, usually requiring only a small incision in the groin or wrist. This results in shorter recovery times and reduced discomfort for the patient.
-
Real-time Monitoring: Coronary angiography offers real-time monitoring of blood flow and allows immediate intervention if a significant blockage is detected during the procedure.
-
Safe and Effective: With advancements in technology and medical expertise, coronary angiography is a safe and effective diagnostic tool that has saved countless lives.
The Coronary Angiography Process:
-
Preparation: Before the procedure, patients may need to fast and discontinue certain medications. The healthcare team will provide specific instructions based on individual needs.
-
Access: A small, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted through a blood vessel, typically in the groin or wrist, and guided through the arteries to the heart.
-
Contrast Injection: A contrast dye is injected through the catheter into the coronary arteries. This dye is visible on X-rays and helps highlight any blockages.
-
Imaging: X-ray images are captured as the dye circulates through the coronary arteries, allowing the cardiologist to assess blood flow and identify blockages.
-
Results and Discussion: The cardiologist interprets the images and discusses the findings with the patient. Treatment options and recommendations are made based on the results.
Benefits of Coronary Angiography:
-
Accurate Diagnosis: Coronary angiography provides a definitive diagnosis of coronary artery disease, guiding personalized treatment.
-
Timely Intervention: It allows for timely intervention, reducing the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications.
-
Minimally Invasive: It is a minimally invasive procedure, which means less discomfort and shorter recovery times for patients.
-
Preventive Measures: Early detection through angiography enables the implementation of preventive measures to reduce the progression of heart disease.